Urinary Incontinence
Urinary Incontinence in Pune
What Is Urinary Incontinence?
Urinary Incontinence is a leaking of urine that refers to the loss of bladder control, varying from a slight loss of urine after sneezing, coughing or laughing, to a complete inability to control urination. This problem can include diseases affecting the bladder, urethra, ureters, kidneys, and adrenal glands. And Dr. Amol Talaulikar is one of the best doctor for urinary incontinence in Pune. Urinary incontinence can have causes that aren’t because of underlying disease. Examples include intoxication, unavailability of bathrooms, coughing, sneezing, extreme anxiety, or intense laughter. See a doctor immediately if you face any of the following symptoms:-
- Suddenly begin leaking urine
- Experience additional urinary symptoms
- Are excessively thirsty and frequently need to urinate
What Is Stress Incontinence?
Stress incontinence occurs when it gets extra pressure on your full bladder — for example, pressure from an activity like coughing, sneezing, laughing, running, or lifting — causes you to leak urine. The leakage stops when the activity stops. Stress incontinence is fairly common among women. It’s caused by weakness in the muscles and tissues that surround the bladder and urethra. This weakness prevents the urethra from closing, and then urine leaks out. The support provided by TVT or TOT tape surgery can often get relieved or correct this leakage.
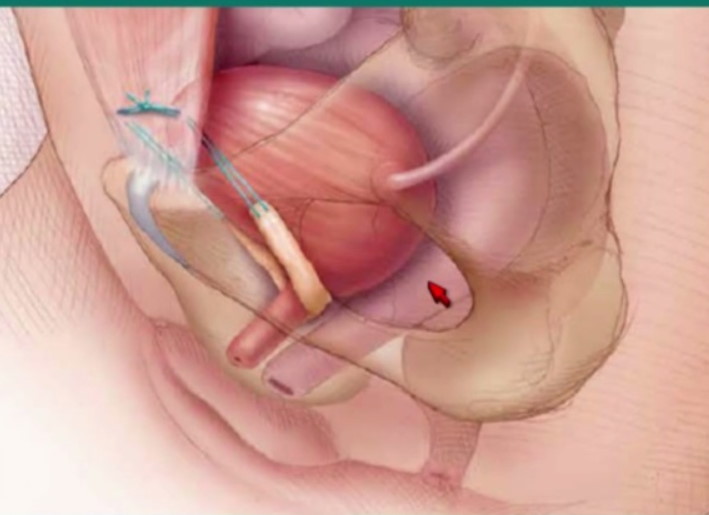
TVT and TOT Tape Surgery in Pune
What is it?
TVT (tension-free vaginal tape) and TOT (trans obturator tape) procedures are used to lift a woman’s sagging bladder or urethra into a normal position. The procedures place a narrow band of tape under the urethra. The tape supports the urethra and bladder like a hammock. Your doctor may recommend a TVT or TOT surgery to treat urinary incontinence.
How is TVT and TOT Tape Surgery Done?
TVT and TOT procedures are called minimally invasive because unlike “open” surgeries, they require only very small incisions (cuts) in the groin, lower abdomen, and vagina. During the procedure, the surgeon passes the tape — a narrow band of synthetic material — through these cuts, slinging it around the urethra to lift and support the urethra and bladder. The surgeon adjusts the tape during surgery to provide the right amount of support. After the surgery, the tape stays in place. The tape is held in place by friction between the tape and the surrounding tissues, and the tape does not protrude outside your body. after the procedure small stitches that close the incisions slowly dissolve in some days.
Risks and Potential Complications of TVT and TOT Surgery.
- A bladder that is slow to empty (usually only a temporary effect, but if needed may be helped by loosening the tape around the urethra)
- Blood clots in the veins or lungs
- Infection in the urinary tract, or at the site of the incision or stitches
- Bleeding during or after surgery
- Injury to the urethra, ureters, bladder, vagina, or surrounding nerves
- Problems related to anesthesia
- The body may reject the tape material, or the material may wear away the tissue of the urethra or vagina
Dr. Amol Talaulikar is the best Doctor for TVT and TOT Tape Surgery & Urinary Incontinence in Pune. Visit Now